转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6194356.html
基本思想
归并排序(MERGE-SORT)是利用归并的思想实现的排序方法,该算法采用经典的分治(divide-and-conquer)策略(分治法将问题分(divide)成一些小的问题然后递归求解,而治(conquer)的阶段则将分的阶段得到的各答案”修补”在一起,即分而治之)。
分而治之
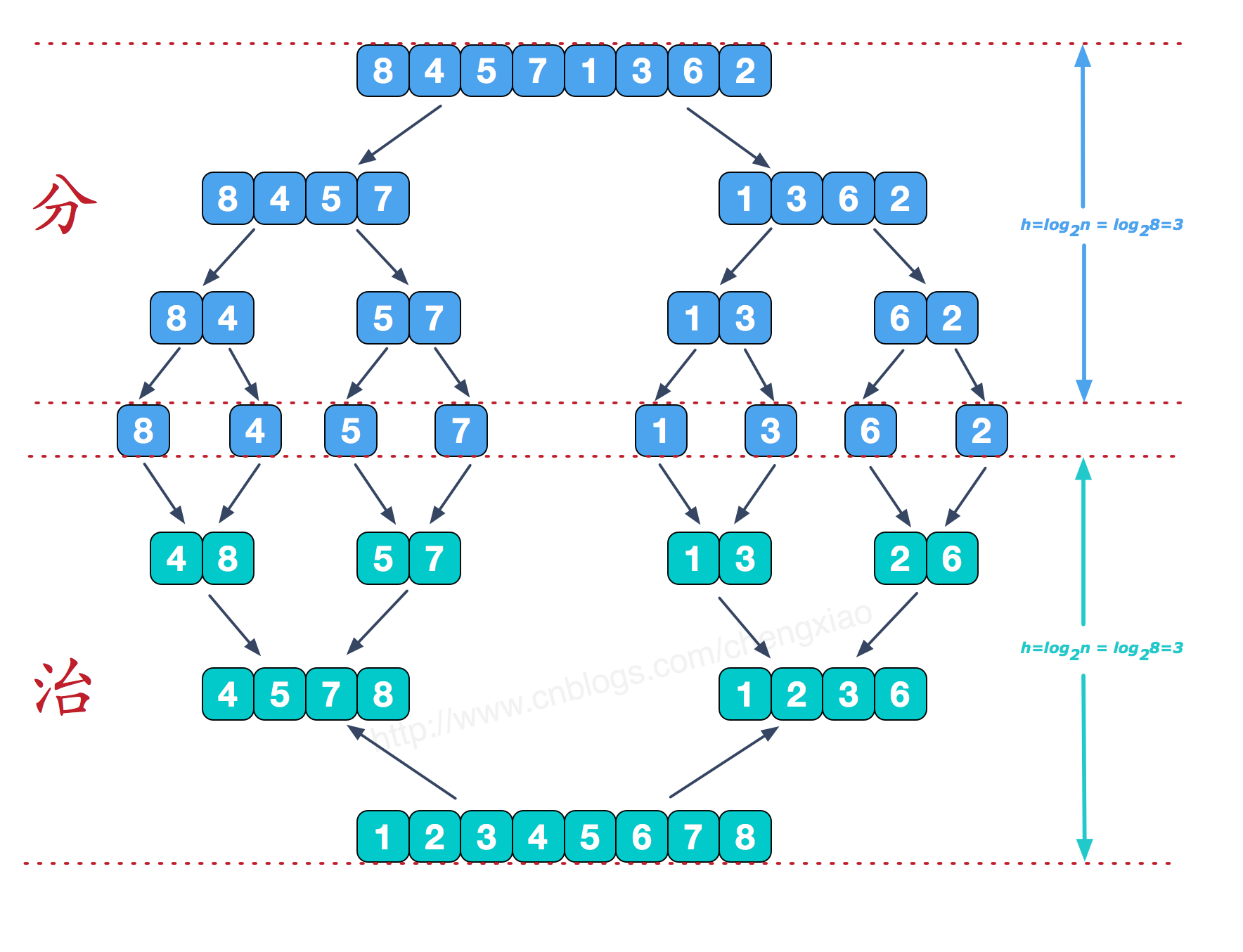
可以看到这种结构很像一棵完全二叉树,本文的归并排序我们采用递归去实现(也可采用迭代的方式去实现)。分阶段可以理解为就是递归拆分子序列的过程,递归深度为log2n。
合并相邻有序子序列
再来看看治阶段,我们需要将两个已经有序的子序列合并成一个有序序列,比如上图中的最后一次合并,要将[4,5,7,8]和[1,2,3,6]两个已经有序的子序列,合并为最终序列[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8],来看下实现步骤。
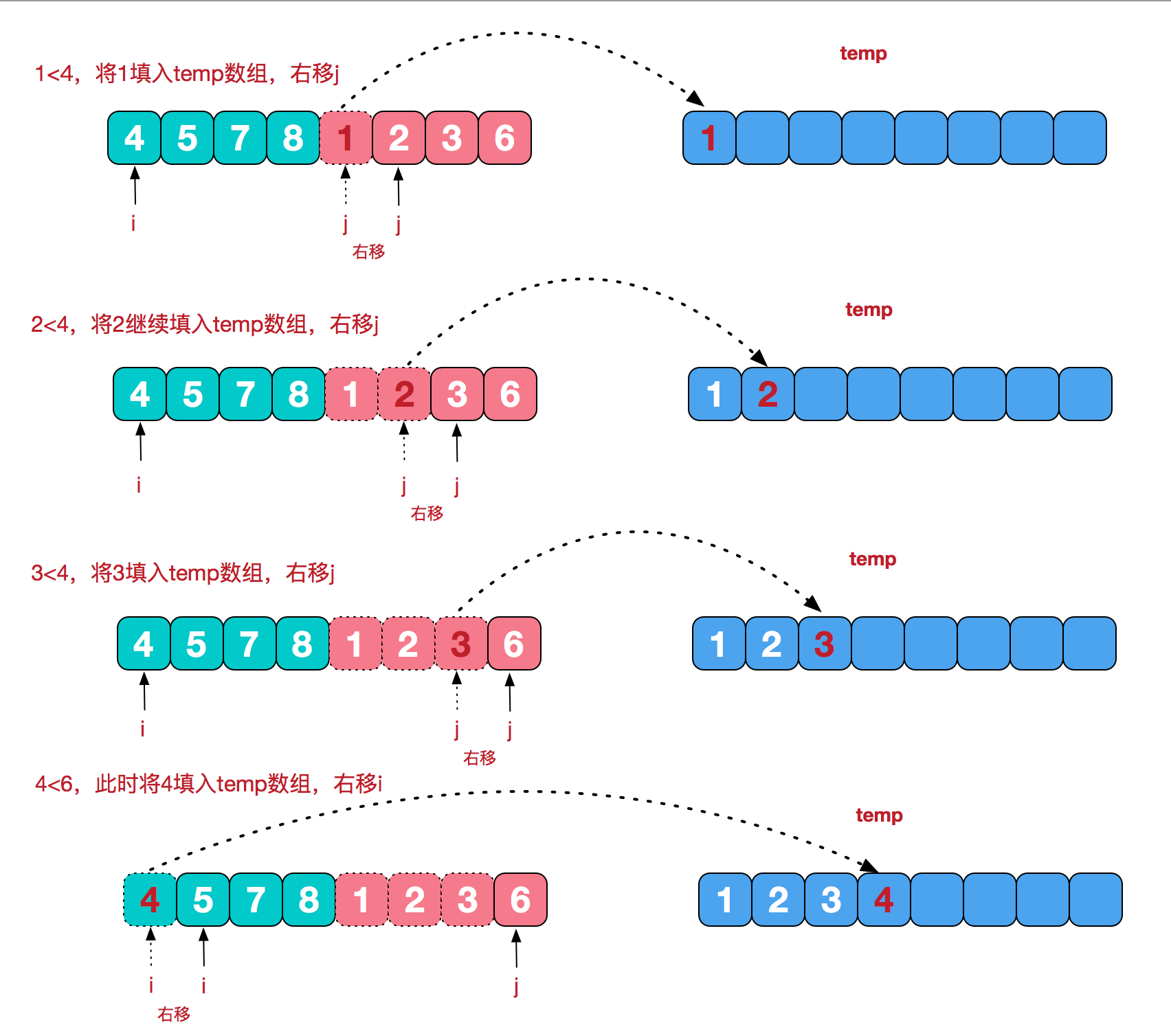
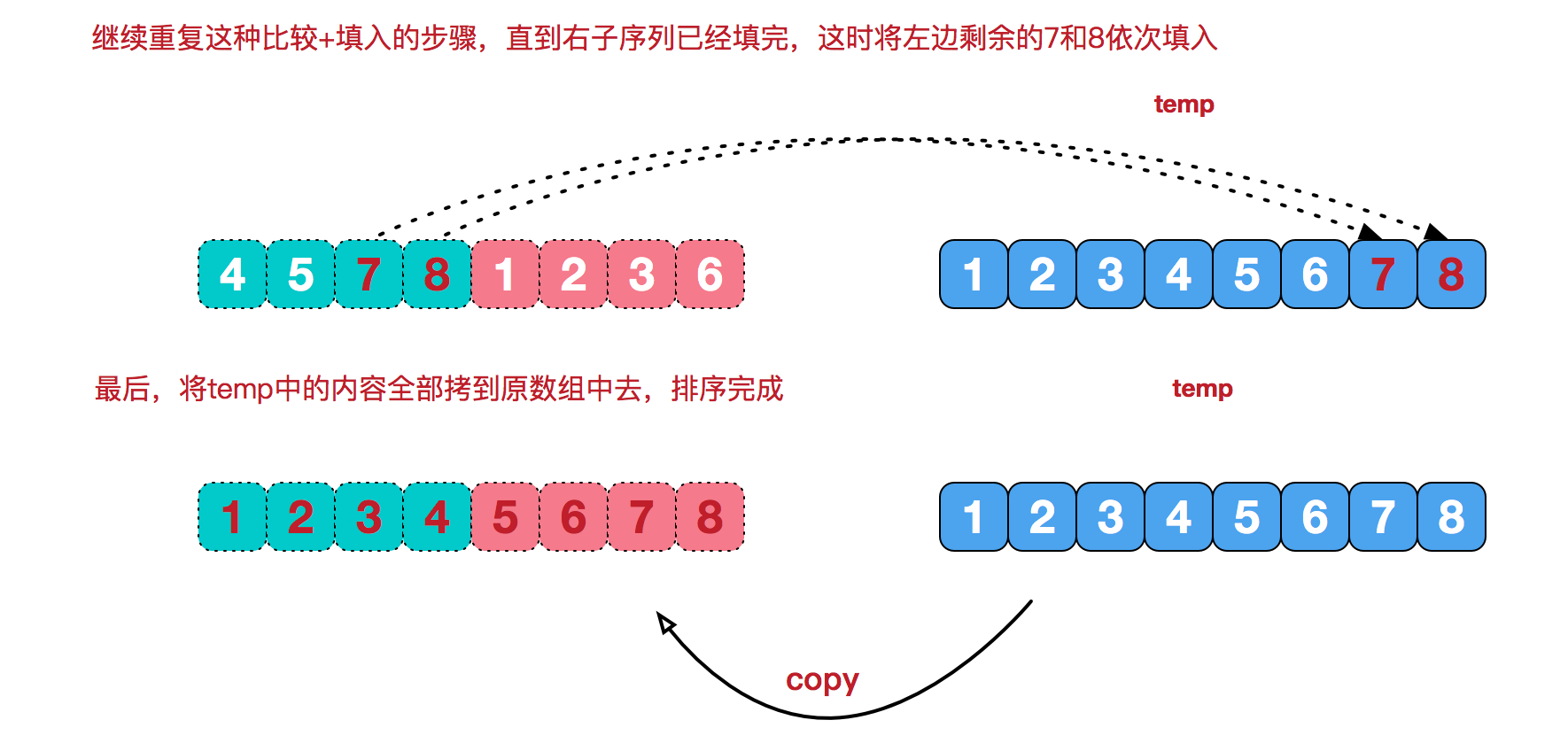
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| package sortdemo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String []args){
int []arr = {9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void sort(int []arr){
int []temp = new int[arr.length];
sort(arr,0,arr.length-1,temp);
}
private static void sort(int[] arr,int left,int right,int []temp){
if(left<right){
int mid = (left+right)/2;
sort(arr,left,mid,temp);
sort(arr,mid+1,right,temp);
merge(arr,left,mid,right,temp);
}
}
private static void merge(int[] arr,int left,int mid,int right,int[] temp){
int i = left;
int j = mid+1;
int t = 0;
while (i<=mid && j<=right){
if(arr[i]<=arr[j]){
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}else {
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid){
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}
while(j<=right){
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
t = 0;
while(left <= right){
arr[left++] = temp[t++];
}
}
}
|
执行结果
1
| [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
|
最后
归并排序是稳定排序,它也是一种十分高效的排序,能利用完全二叉树特性的排序一般性能都不会太差。java中Arrays.sort()采用了一种名为TimSort的排序算法,就是归并排序的优化版本。从上文的图中可看出,每次合并操作的平均时间复杂度为O(n),而完全二叉树的深度为|log2n|。总的平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。而且,归并排序的最好,最坏,平均时间复杂度均为O(nlogn)。






